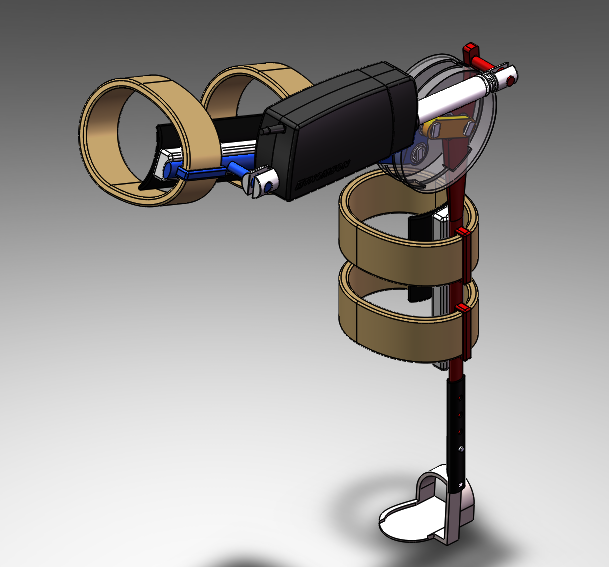
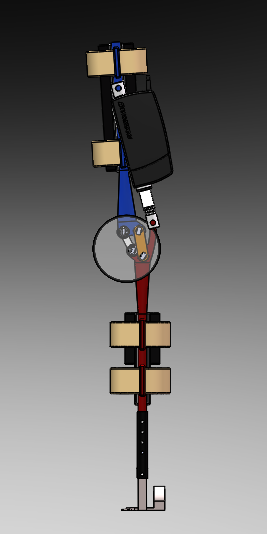
We found some useful information on the internet, which helped us to understand better how the other commercial companies faced with similar problems. They are shown in this "Inspiration" section:
Ekso Bionics develop and manufacture powered exoskeleton bionic devices that can be strapped on as wearable robots to enhance the strength, mobility, and endurance of soldiers and paraplegics. These assistive robots have a variety of applications in the medical, military, industrial, and consumer markets. It enables individuals with any amount of lower extremity weakness, including those who are paralyzed, to stand up and walk.
The company's first commercially available product is called called Ekso. Ekso Bionics is the original developer of HULC, now under military development by Lockheed Martin, and the current developers of Ekso (formerly eLEGS), which allows wheelchair users to stand and walk.
http://www.eksobionics.com/
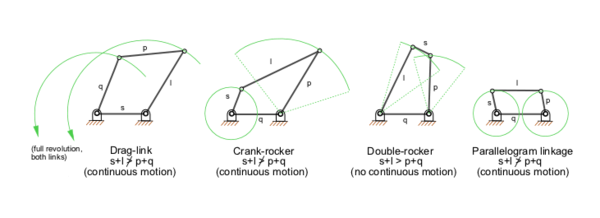
2、Four-bar Internal Knee System
More than 100 individual knee mechanisms are commercially available for the North American amputee population. Classifications for prosthetic knees have been proposed previously, but there are two basic knee categories of kinematic function into which prosthetic knees fall: single-axis knees and polycentric knees. Prosthetists should be aware of several key differences between these two classes of knees to make informed decisions regarding prescriptions of prosthetic knees for their patients.
Single-axis knees have a single axis of rotation about which the shank rotates with respect to the thigh. Polycentric knees, on the other hand, are characterized by a center of rotation that varies with the knee-flexion angle. The center of rotation, more appropriately called the instantaneous center of rotation, is simply the point about which the shank and foot rotate as the knee flexes. Polycentric knees are becoming increasingly popular among prosthetists for transfemoral amputee prostheses.
The most common type of polycentric knee is the four-bar linkage knee, so-called because it has four axes of rotation connected by four rigid linkages. The polycentric nature of four-bar linkage knees accounts for two key advantages: stance-phase stability and knee-flexion cosmesis. A lesser known distinction of four-bar linkage knees is their inherent ability to provide greater foot clearance than single-axis knees for a given knee-flexion angle. This additional floor clearance allows the amputee to walk with less concern for floor clearance during prosthetic swing. This article focuses primarily on floor clearance issues of four-bar and single-axis knees but also includes brief discussions of stance-phase stability and cosmesis.